最近年底了,有点忙,拖更了一个月
进阶算法之排序和搜索
排序和搜索是什么?
- 排序:把某个乱序的数组变成升序或者降序的数组
- 搜索:找出数组中某个元素的下标
JS中的排序和搜索
- JS中的排序:数组的sort方法
- JS中的搜索:数组的indexOf方法
排序算法:
- 冒泡排序
- 选择排序
- 插入排序
- 归并排序
- 快速排序
- ...
搜索算法
- 顺序搜索
- 二分搜索
- ...
JavaScript实现:冒泡排序
冒泡排序的思路
- 比较所有相邻元素,如果第一个比第二个大,则交换他们
- 一轮下来,可以保证最后一个数是最大的
- 执行n-1轮,就可以完成排序
各类排序的思路动画演示 https://visualgo.net/zh
冒泡排序的时间复杂度
- 两个嵌套循环
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
// 冒泡排序
Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function () {
console.log(this);
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i += 1) {
for (let j = 0; j < this.length - 1 - i; j += 1) {
console.log(this[j], this[j + 1])
if (this[j] > this[j + 1]) {
const temp = this[j];
this[j] = this[j + 1];
this[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
arr.bubbleSort();JavaScript实现:选择排序
- 找到数组中的最小值,选中它并将其放置在第一位
- 接着找到第二小的值,选中它并将其放置在第二位
- 以此类推,执行n - 1 轮
选择排序的时间复杂度
- 两个嵌套循环
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
// 选择排序的实现
Array.prototype.selectionSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i += 1) {
let indexMin = i;
for (let j = i; j < this.length; j += 1) {
if (this[j] < this[indexMin]) {
indexMin = j;
}
}
if (indexMin !== i) {
const temp = this[i];
this[i] = this[indexMin];
this[indexMin] = temp;
}
}
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
arr.selectionSort();JavaScript实现:插入排序
- 从第二个数开始往前比
- 比它大就往后排
- 以此类推进行到最后一个数
插入排序的时间复杂度
- 两个嵌套循环
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
// 插入排序的实现
Array.prototype.insertionSort = function () {
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i += 1) {
const temp = this[i];
let j = i;
while (j > 0) {
if (this[j - 1] > temp) {
this[j] = this[j - 1];
} else {
break;
}
j -= 1;
}
this[j] = temp;
}
};
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
arr.insertionSort();JavaScript实现:归并排序
- 分:把数组劈成两半,在递归地对子数组进行"分"操作,直到分成一个个单独的数
- 合:把两个数合并为有序数组,再对有序数组进行合并,直到全部子数组合并为一个完整数组
合并两个有序数组
- 新建一个空数组res,用于存放最终排序后的数组
- 比较两个有序数组的头部,较小者出队并推入res中
- 如果两个数组还有值,就重复第二步
归并排序的时间复杂度
- 分的时间复杂度是O(logN)
- 合的时间复杂度:O(n)
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogN)
// 归并排序的实现
Array.prototype.mergeSort = function () {
// 分
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const mid = Math.floor(arr.length / 2); // 获取中间下标
const left = arr.slice(0, mid); // 获取左边数组
const right = arr.slice(mid, arr.length); // 获取右边数组
const orderLeft = rec(left); // 左边数组有序
const orderRight = rec(right); // 右边数组有序
const res = [];
while (orderLeft.length || orderRight.length) {
if (orderLeft.length && orderRight.length) {
// 比较队头
res.push(orderLeft[0] < orderRight[0] ? orderLeft.shift() : orderRight.shift());
} else if (orderLeft.length) {
res.push(orderLeft.shift());
} else if (orderRight.length) {
res.push(orderRight.shift());
}
}
return res;
}
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
})
}
const arr = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
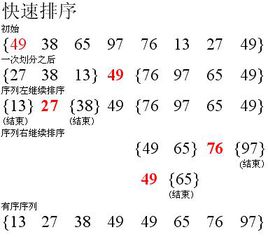
arr.mergeSort();JavaScript实现:快速排序
- 分区:从数组中任意选择一个“基准”,所有比基准小的元素放在基准前面,比基准大的元素放在基准的后面
- 递归:递归地对基准前后的子数组进行分区
快速排序的时间复杂度
- 递归的时间复杂度是O(logN)
- 分区操作的时间复杂度:O(n)
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogN)
// 快速排序的实现
Array.prototype.quickSort = function () {
const rec = (arr) => {
if (arr.length === 1) {
return arr;
}
const left = [];
const right = [];
const mid = arr[0];
for (let i = 1; i < arr.length; i += 1) {
if (arr[i] < mid) {
left.push(arr[i]);
} else {
right.push(arr[i]);
}
}
return [...rec(left), mid, ...rec(right)];
}
const res = rec(this);
res.forEach((n, i) => {
this[i] = n;
});
}
const arr = [2, 4, 5, 3, 1];
arr.quickSort();
console.log(arr)JavaScript实现:顺序搜索
- 遍历数组
- 找到跟目标值相等的元素,就返回它的下标
- 遍历结束后,如果没有搜索到目标值,就返回-1
顺序搜索的时间复杂度
- 遍历数组是一个循环操作
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
// 顺序搜索的实现
Array.prototype.sequentialSearch = function (item) {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i += 1) {
if (this[i] === item) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
const res = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].sequentialSearch(3);Javascript实现:二分搜索
- 从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则搜索结束
- 如果目标值大于或者小于中间元素,则在大于或小于中间元素的那一半数组中搜索
二分搜索的时间复杂度
- 每一次比较都使搜索范围缩小一半
- 时间复杂度:O(logN)
// 二分搜索的实现
Array.prototype.binarySearch = function (item) {
let low = 0;
let high = this.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const element = this[mid];
if (element < item) {
low = mid + 1;
} else if (element > item) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
const res = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].binarySearch(5);LeetCode #21 合并两个有序链表
将两个升序链表合并为一个新的 升序 链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
示例:
- 输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
- 输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
解题思路:
- 与归并排序中的合并两个有序数组很相似
- 将数组替换成链表就能解决此题
解题步骤:
- 新建一个新链表,作为返回结果
- 用指针遍历两个有序链表,并比较两个链表的当前节点,较小者先接入新链表,并将指针后移一步
- 链表遍历结束,返回新链表
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)即链表1和链表2的长度之和
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {ListNode} l1
* @param {ListNode} l2
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeTwoLists = function(l1, l2) {
const res = new ListNode(0); // 新建新链表
let p = res;
let p1 = l1; // 指针1:不停指向新链表的最后一个节点。
let p2 = l2;
while(p1 && p2){
// 链表1当前节点值小于链表2当前节点值
if(p1.val < p2.val){
p.next = p1; // p1接到新链表最后一个节点上
p1 = p1.next; // 移动
}else{
p.next = p2; // p2接到新链表最后一个节点上
p2 = p2.next;
}
p = p.next; // 保证p永远指向新链表最后一个节点上
}
if(p1){
p.next = p1;
}
if(p2){
p.next = p2;
}
return res.next; // 输出链表的头部上一个节点
};LeetCode #374 猜数字大小
猜数字游戏的规则如下:
每轮游戏,我都会从 1 到 n 随机选择一个数字。 请你猜选出的是哪个数字。
如果你猜错了,我会告诉你,你猜测的数字比我选出的数字是大了还是小了。
你可以通过调用一个预先定义好的接口 int guess(int num) 来获取猜测结果,返回值一共有 3 种可能的情况(-1,1 或 0):
- -1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字小 pick < num
- 1:我选出的数字比你猜的数字大 pick > num
- 0:我选出的数字和你猜的数字一样。恭喜!你猜对了!pick == num
示例 :
- 输入:n = 10, pick = 6
- 输出:6
- 输入:n = 1, pick = 1
- 输出:1
- 输入:n = 2, pick = 1
- 输出:1
- 输入:n = 2, pick = 2
- 输出:2
提示:
- 1 <= n <= 2^31 - 1
- 1 <= pick <= n
解题思路:
- 二分搜索
- 调用guess函数,来判断中间元素是否是目标值
解题步骤:
- 从数组的中间元素开始,如果中间元素正好是目标值,则搜索过程结束
- 如果目标值大于或者小于中间元素,则在数组大于或小于中间元素的那一半中查找
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(logN)
- 空间复杂度:O(1)
/**
* Forward declaration of guess API.
* @param {number} num your guess
* @return -1 if num is lower than the guess number
* 1 if num is higher than the guess number
* otherwise return 0
* var guess = function(num) {}
*/
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var guessNumber = function(n) {
let low = 1;
let high = n;
while(low <= high){
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
const res = guess(mid);
// console.log('mid', mid);
// console.log('res', res);
if(res === 0){
return mid;
} else if (res === 1){
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
};排序与搜索-章节总结
排序和搜索是什么?
- 排序:把某个乱序的数组变成升序或者降序的数组
- 搜索:找出数组中某个元素的下标
JS中的排序和搜索
- JS中的排序:数组的sort方法
- JS中的搜索:数组的indexOf方法
排序算法:
- 冒泡排序 O(n²)
- 选择排序 O(n²)
- 插入排序 O(n²)
- 归并排序 O(nlogn)
- 快速排序 O(nlogn)
搜索算法
- 顺序搜索 O(n)
- 二分搜索 O(logn)
阶段性思考
- Chrome 最新的Array.prototype.sort用的是什么排序算法?
- 用二分搜索算法求x的平方根。题目链接:http://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sqrtx/

Comments | NOTHING