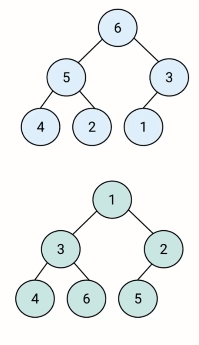
堆是什么?
- 堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树
- 所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或小于等于(最小堆)它的子节点
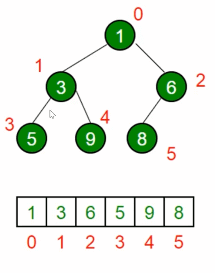
JS中的堆
- JS中通常用数组表示堆
- 左侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 1
- 右侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 2
- 父节点位置是(index - 1)/ 2 的商
堆的应用
- 堆能高效。快速地找出最大值和最小值,时间复杂度:O(1)
- 找出第k个最大(小)元素
第k个最大(最小)元素
- 构建一个最小(最大)堆,并将元素依次插入堆中
- 当堆的容量超过k,就删除堆顶
- 插入结束后,堆顶就是第k个最大元素
JavaScript 实现最小堆类
实现步骤:
- 在类里,声明一个数组,用来装元素
- 主要方法:插入,删除堆顶,获取堆顶,获取堆大小
插入:
- 将值插入堆的底部,即数组的尾部
- 然后上移:将这个值和它的父节点进行交换,直到父节点小于等于这个插入的值
- 大小为k的堆中插入元素的时间复杂度为O(logK)
删除堆顶
- 用数组尾部元素替换堆顶(直接删除堆顶会破坏堆结构)
- 然后下移:将新堆顶和它的子节点进行交换,直到子节点大于等于这个新堆顶
- 大小为k的堆中删除堆顶的时间复杂度为O(logK)
获取堆顶和堆的大小
- 获取堆顶:返回数组的头部
- 获取堆的大小:返回数组的长度
// 最小堆实现
class MinHeap{
constructor(){
this.heap = [];
}
// 交换
swap(i1, i2){
const temp = this.heap[i1];
this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2];
this.heap[i2] = temp;
}
getParentIndex(i){
// return Math.floor((i - 1) / 2)
// 进阶写法,二进制操作,二进制右移一位,即除以2
// 父节点位置是(index - 1)/ 2 的商
return (i - 1) >> 1;
}
getLeftIndex(i){
// 左侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 1
return i * 2 + 1;
}
getRightIndex(i){
// 右侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 2
return i * 2 + 2;
}
shiftUp(index){
if(index == 0){ //如果是堆顶,就不再上移
return;
}
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
if(this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]){
this.swap(parentIndex, index);
this.shiftUp(parentIndex);
}
}
shiftDown(index){
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index);
if(this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]){
this.swap(leftIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(leftIndex);
}
if(this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]){
this.swap(rightIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(rightIndex);
}
}
// 插入
insert(value){
this.heap.push(value);
// 上移(保证堆的结构正确)
this.shiftUp(this.heap.length-1);
}
pop(){
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
this.shiftDown(0);
}
// 获取堆顶
peek(){
return this.heap[0];
}
// 获取堆的大小
size(){
return this.heap.length;
}
}
const h = new MinHeap();
h.insert(3);
h.insert(2);
h.insert(1);
h.pop();LeetCode #215 数组中的第k个最大元素
在未排序的数组中找到第 k 个最大的元素。请注意,你需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
示例:
- 输入: [3,2,1,5,6,4] 和 k = 2
- 输出: 5
- 输入: [3,2,3,1,2,4,5,5,6] 和 k = 4
- 输出: 4
解题思路:
- 看大“第k个最大元素”
- 考虑使用最小堆
解题步骤:
- 构建一个最小堆,并依次把数组的值插入堆中
- 当堆的容量超过k,就删除堆顶
- 插入结束后,堆顶就是第k个最大元素
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n * logk) (上移和下移操作是递归操作)
- 空间复杂度:O(k)(实现的是堆,数组的就是它的空间复杂度)
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
// 最小堆实现
class MinHeap{
constructor(){
this.heap = [];
}
// 交换
swap(i1, i2){
const temp = this.heap[i1];
this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2];
this.heap[i2] = temp;
}
getParentIndex(i){
// return Math.floor((i - 1) / 2)
// 进阶写法,二进制操作,二进制右移一位,即除以2
// 父节点位置是(index - 1)/ 2 的商
return (i - 1) >> 1;
}
getLeftIndex(i){
// 左侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 1
return i * 2 + 1;
}
getRightIndex(i){
// 右侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 2
return i * 2 + 2;
}
shiftUp(index){
if(index == 0){ //如果是堆顶,就不再上移
return;
}
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
if(this.heap[parentIndex] > this.heap[index]){
this.swap(parentIndex, index);
this.shiftUp(parentIndex);
}
}
shiftDown(index){
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index);
if(this.heap[leftIndex] < this.heap[index]){
this.swap(leftIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(leftIndex);
}
if(this.heap[rightIndex] < this.heap[index]){
this.swap(rightIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(rightIndex);
}
}
// 插入
insert(value){
this.heap.push(value);
// 上移(保证堆的结构正确)
this.shiftUp(this.heap.length-1);
}
pop(){
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
this.shiftDown(0);
}
// 获取堆顶
peek(){
return this.heap[0];
}
// 获取堆的大小
size(){
return this.heap.length;
}
}
var findKthLargest = function(nums, k) {
const heap = new MinHeap();
// 把数组中的值依次插入到堆中
nums.forEach(n => {
heap.insert(n);
// 当发现堆的大小超过k,部分元素出去
if(heap.size() > k){
heap.pop();
}
})
// console.log(heap)
return heap.peek();
};LeetCode #347 前k个高频元素
给定一个非空的整数数组,返回其中出现频率前 k 高的元素。
示例:
- 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2
- 输出: [1,2]
- 输入: nums = [1], k = 1
- 输出: [1]
提示:
你可以假设给定的 k 总是合理的,且 1 ≤ k ≤ 数组中不相同的元素的个数。
你的算法的时间复杂度必须优于 O(n log n) , n 是数组的大小。
题目数据保证答案唯一,换句话说,数组中前 k 个高频元素的集合是唯一的。
你可以按任意顺序返回答案
解题思路一:(统计所有的元素出现的频率):
- 利用map记录所有元素出现的频率
- 对map进行转数组,然后降序排序
- 然后通过找出k之前的频率返回出对应的元素
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogn),原生排序最优的时间复杂度是 O(nlogn)。不符合题目要求
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number[]}
*/
var topKFrequent = function(nums, k) {
// 实现: 统计所有元素出现的次数
const map = new Map();
nums.forEach(n => {
map.set(n, map.has(n) ? map.get(n) + 1 : 1);
})
/**
* 排序
* 1. map 转数组
* 2. 降序排序
*/
const list = Array.from(map).sort((a,b) => b[1] - a[1]);
// console.log(list)
// console.log(map);
return list.slice(0, k).map(n=>{
return n[0]
})
};解题思路二:(堆的思路)
- 建立一个最小堆
- 把元素及频率插入到堆中
- 按照频率排序
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n logk)。因为1<= k <= n 所以 n logk < n * logn。符合题意
- 空间复杂度:O(n)。字典复杂度是n 堆的复杂度是k ,k<n
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @param {number} k
* @return {number[]}
*/
// 最小堆实现
class MinHeap{
constructor(){
this.heap = [];
}
// 交换
swap(i1, i2){
const temp = this.heap[i1];
this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2];
this.heap[i2] = temp;
}
getParentIndex(i){
// return Math.floor((i - 1) / 2)
// 进阶写法,二进制操作,二进制右移一位,即除以2
// 父节点位置是(index - 1)/ 2 的商
return (i - 1) >> 1;
}
getLeftIndex(i){
// 左侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 1
return i * 2 + 1;
}
getRightIndex(i){
// 右侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 2
return i * 2 + 2;
}
shiftUp(index){
if(index == 0){ //如果是堆顶,就不再上移
return;
}
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
if(this.heap[parentIndex] && this.heap[parentIndex].value > this.heap[index].value){
this.swap(parentIndex, index);
this.shiftUp(parentIndex);
}
}
shiftDown(index){
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index);
if(this.heap[leftIndex] && this.heap[leftIndex].value < this.heap[index].value){
this.swap(leftIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(leftIndex);
}
if(this.heap[rightIndex] && this.heap[rightIndex].value < this.heap[index].value){
this.swap(rightIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(rightIndex);
}
}
// 插入
insert(value){
this.heap.push(value);
// 上移(保证堆的结构正确)
this.shiftUp(this.heap.length-1);
}
pop(){
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
this.shiftDown(0);
}
// 获取堆顶
peek(){
return this.heap[0];
}
// 获取堆的大小
size(){
return this.heap.length;
}
}
var topKFrequent = function(nums, k) {
// 实现: 堆的思路,最小堆
const map = new Map();
nums.forEach(n => {
map.set(n, map.has(n) ? map.get(n) + 1 : 1)
})
const heap = new MinHeap();
map.forEach((value, key)=>{
heap.insert({value, key});
// 保证最小堆的尺寸永远小于k
if(heap.size() > k){
// 剔除最小的
heap.pop();
}
})
// console.log(heap)
return heap.heap.map(obj => obj.key)
};LeetCode #23 合并k个排序链表
给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
示例 1:
- 输入:lists = [[1,4,5],[1,3,4],[2,6]]
- 输出:[1,1,2,3,4,4,5,6]
解释:链表数组如下:
[ 1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6 ] 将它们合并到一个有序链表中得到。 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6示例 2:
- 输入:lists = []
- 输出:[]
示例 3:
- 输入:lists = [[]]
- 输出:[]
提示:
- k == lists.length
- 0 <= k <= 10^4
- 0 <= lists[i].length <= 500
- -10^4 <= listsi <= 10^4
- lists[i] 按 升序 排列
- lists[i].length 的总和不超过 10^4
解题思路:
- 新链表的下一个节点一定是k个链表头中的最小节点
- 考虑选择使用最小堆
解题步骤:
- 构建一个最小堆,并依次把链表头插入堆中
- 弹出堆顶接到输出链表,并将堆顶所在链表的新链表头插入堆中
- 堆元素全部弹出,合并工作就完成了。
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n * logk)
- 空间复杂度:O(k)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* function ListNode(val, next) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.next = (next===undefined ? null : next)
* }
*/
// 最小堆实现
class MinHeap{
constructor(){
this.heap = [];
}
// 交换
swap(i1, i2){
const temp = this.heap[i1];
this.heap[i1] = this.heap[i2];
this.heap[i2] = temp;
}
getParentIndex(i){
// return Math.floor((i - 1) / 2)
// 进阶写法,二进制操作,二进制右移一位,即除以2
// 父节点位置是(index - 1)/ 2 的商
return (i - 1) >> 1;
}
getLeftIndex(i){
// 左侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 1
return i * 2 + 1;
}
getRightIndex(i){
// 右侧子节点的位置是 2 * index + 2
return i * 2 + 2;
}
shiftUp(index){
if(index == 0){ //如果是堆顶,就不再上移
return;
}
const parentIndex = this.getParentIndex(index);
if(this.heap[parentIndex] && this.heap[parentIndex].val > this.heap[index].val){
this.swap(parentIndex, index);
this.shiftUp(parentIndex);
}
}
// 下移
shiftDown(index){
const leftIndex = this.getLeftIndex(index);
const rightIndex = this.getRightIndex(index);
if(this.heap[leftIndex] && this.heap[leftIndex].val < this.heap[index].val){
this.swap(leftIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(leftIndex);
}
if(this.heap[rightIndex] && this.heap[rightIndex].val < this.heap[index].val){
this.swap(rightIndex, index);
this.shiftDown(rightIndex);
}
}
// 插入
insert(value){
this.heap.push(value);
// 上移(保证堆的结构正确)
this.shiftUp(this.heap.length-1);
}
// 弹出堆顶
pop(){
if(this.size() === 1){
return this.heap.shift();
}
const top = this.heap[0];
this.heap[0] = this.heap.pop();
this.shiftDown(0);
return top;
}
// 获取堆顶
peek(){
return this.heap[0];
}
// 获取堆的大小
size(){
return this.heap.length;
}
}
/**
* @param {ListNode[]} lists
* @return {ListNode}
*/
var mergeKLists = function(lists) {
// 输出链表
const res = new ListNode(0);
let p = res; // 声明指针,接入输入链表
// 新建最小堆
const heap = new MinHeap();
// 把链表的头部节点都放在最小堆中
lists.forEach(list => { // 循环所有链表
if(list){
heap.insert(list);
}
})
while(heap.size()){
// 弹出堆顶,即链表们中头部节点最小值
const n = heap.pop();
p.next = n;
p = p.next; // 指针向下走
if(n.next){ // 最小节点的next 插入到堆中
heap.insert(n.next);
}
}
return res.next;
};堆-章节总结
- 堆是一种特殊的完全二叉树
- 所有的节点都大于等于(最大堆)或者小于等于(最小堆)它的子节点
- JS中通常用数组表示堆
- 堆能高效,快速地找出最大值和最小值,时间复杂度:O(1)
- 找出第k个最大(小)元素

Comments | NOTHING