树是什么?
- 一种分层数据的抽象模型
- 前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM树,级联选择、树形控件
- JS中没有树,但是可以用Object和Array构建树
- 树的常用操作:深度/广度优先遍历、先中后序遍历
什么是树的深度/广度优先遍历?
- 深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索树的分支
- 广度优先遍历:先访问离根节点最近的节点
深度优先遍历算法口诀
- 访问根节点
对根节点的children挨个进行深度优先遍历
const tree = { val: 'a', children: [ { val: 'b', children: [ { val: 'd', children: [] }, { val: 'e', children: [] } ] }, { val: 'c', children: [ { val: 'f', children: [] }, { val: 'g', children: [] } ] } ] } const dfs = (root) => { console.log(root.val); // root.children.forEach((child)=>{ // dfs(child) // }) // 优化写法 root.children.forEach(dfs) } dfs(tree)
广度优先遍历算法口诀
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队
- 把对头出队并访问
- 把对头的children挨个入队
- 重复第二三步,知道队列为空
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: []
},
{
val: 'e',
children: []
}
]
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: []
},
{
val: 'g',
children: []
}
]
}
]
}
const bfs = (root)=>{
const queue = [root];
while(queue.length>0){
const n = queue.shift();
console.log(n.val)
n.children.forEach(child=>{
queue.push(child);
})
}
}
bfs(tree)二叉树的先中后遍历
二叉树是什么?
- 树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点
- 在JS中通常用Object来模拟二叉树
先序遍历算法口诀
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的左子树进行先序遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行先序遍历
// 二叉树 bt.js
const bt = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null
}
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
module.exports = bt;// 先序遍历
const bt = require('./bt');
const preorder = (root)=> {
if(!root){ return; }
console.log(root.val)
preorder(root.left);
preorder(root.right);
}
preorder(bt);
// 1 2 4 5 3 6 7中序遍历算法口诀
- 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历
// 中序遍历
const bt = require('./bt');
const inorder = (root)=>{
if(!root){ return; }
inorder(root.left);
console.log(root.val);
inorder(root.right);
}
inorder(bt)
// 4 2 5 1 6 3 7后续遍历算法口诀
- 对根节点的左子树进行后续遍历
- 对根节点的右子树进行后续遍历
- 访问根节点
// 后续遍历
const bt = require('./bt');
const postorder = (root)=>{
if(!root){ return; }
postorder(root.left);
postorder(root.right);
console.log(root.val);
}
// postorder(bt)
// 4 5 2 6 7 3 1二叉树的先中后序遍历(非递归版)
// 先序遍历(非递归版)核心思路用堆栈,因为在函授中调用另一个函数其实就是连续的调用堆栈,即递归版的原理
const preorderPlus = (root) =>{
if(!root){ return; }
const stack = [root];
while(stack.length){
const n = stack.pop(); // 最开始访问根节点的值,循环到以后就是部分子树的根节点
console.log(n.val);
// 栈:后进先出 所以需要先推right
if(n.right){// 递归右子树
stack.push(n.right);
}
if(n.left){ // 递归左子树
stack.push(n.left);
}
}
}
preorderPlus(bt)// 中序遍历(非递归版)
const inorderPlus = (root)=>{
if(!root){ return; }
// 核心思路:遍历所有左子树->根节点->右子树
const stack = [];
let p = root; // 指针
while(stack.length || p){ // 循环1,2,3,4
while(p){
// 1.把所有子树丢入栈中
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
// 2.弹出最尽头的节点
const n = stack.pop();
// 3.访问最尽头的节点
console.log(n.val);
// 4.访问右节点(指针指向右节点)
p = n.right;
}
}
inorderPlus(bt)// 后续遍历(非递归版)
const postorderPlus = (root)=>{
// 核心思路:
// 1. 把后续遍历的顺序倒置(左右根->根右左,与先序遍历很像)
// 2. 把先序遍历的访问操作,改成入栈操作
// 3. 利用栈的后进先出特性,子节点逆序输出
if(!root){ return; }
const outputStack = []; // 做倒置操作的堆栈
const stack = [root]; // 函数调用堆栈
while(stack.length){ // 根右左
const n = stack.pop();
outputStack.push(n);
if(n.left){
stack.push(n.left);
}
if(n.right){
stack.push(n.right);
}
}
while(outputStack.length){ // 倒序输出
const n = outputStack.pop();
console.log(n.val);
}
}
postorderPlus(bt) LeetCode #104 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
- 说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
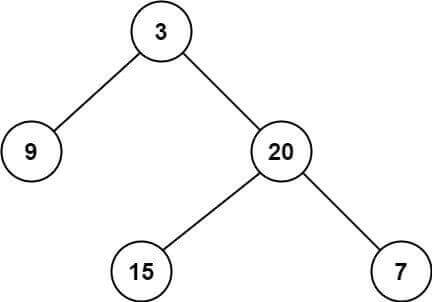
- 示例:给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7返回它的最大深度 3 。
解题思路:
- 求最大深度,考虑使用深度优先遍历
- 在深度优先遍历过程中,记录每个节点所在层级,找出最大层级即可。
解题步骤:
- 新建一个变量记录最大深度
- 深度优先遍历整棵树,并记录每个节点的层级,同时不断刷新最大深度这个变量。
- 遍历结束返回最大深度的变量
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:最坏 O(n)最好 O(logN) (隐形调用了函数堆栈)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {
let deepMax = 0;
const dfs = (node, level)=>{ // level即节点所处层级
if(!node){
return;
}
if(!node.left && !node.right){ // 只在叶子节点时计算最大深度
deepMax = Math.max(deepMax, level)
}
dfs(node.left, level + 1);
dfs(node.right, level + 1);
};
dfs(root,1);
return deepMax;
};LeetCode #111 二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
- 输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
- 输出:2
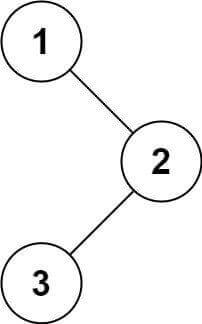
- 输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
- 输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在 [0, 105] 内
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
解题思路:
- 求最小深度,考虑使用广度优先遍历
- 在广度优先遍历过程中,遇到叶子节点,停止遍历,返回节点层级
解题步骤:
- 广度优先遍历整颗树,并记录每个节点的层级
- 遇到叶子节点,返回节点层级,停止遍历
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth = function(root) {
if(!root) {
return 0;
}
const queue = [[root, 1]]; // 新建队列,并把根节点传入
while(queue.length){
const [node, level] = queue.shift(); // 拿出队头,并访问
if(!node.left && !node.right){ // 如果是叶子节点
return level
}
if(node.left){
queue.push([node.left, level + 1]); // 当前节点的孩子节点加入对列
}
if(node.right){
queue.push([node.right,level + 1]);
}
}
};LeetCode #102 二叉树的层序遍历
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例:
二叉树:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]解题思路:
- 层序遍历顺序就是广度优先遍历
- 不过在遍历时候需要记录当前节点所处的层级,方便将其添加到不同的数组中
解题步骤:
- 广度优先遍历(用队列)
- 遍历过程中,记录每个节点的层级,并将其添加到不同的数组中
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)广度优先遍历
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root){ // 保证root节点不为空
return [];
}
// 广度优先遍历
const queue = [[root, 0]]; // 节点,层级
const res = [];
while (queue.length) {
const [node, level] = queue.shift(); // 节点出队,并记录每个节点的层级
// console.log(node.val, level) // 访问节点
if(!res[level]){ // res[level]没值的话,先push一个数组
// 把节点的值按照层级分别push到不同数组,返回
res.push([node.val])
}else{
res[level].push(node.val);
}
// 将节点的孩子节点推进队列
if(node.left){
queue.push([node.left, level + 1])
}
if(node.right){
queue.push([node.right, level + 1])
}
}
return res;
};优化方案:
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if(!root){ // 保证root节点不为空
return [];
}
const queue = [root];
const res = [];
while (queue.length) {
let len = queue.length;
res.push([]);
while(len--){// 优化:保证每次while循环时,老一层级的节点都出队列,其节点的孩子节点们都入队。即保证queue中只有同级节点
const node = queue.shift();
res[res.length - 1].push(node.val);
if(node.left){
queue.push(node.left)
}
if(node.right){
queue.push(node.right)
}
}
}
return res;
};LeetCode #94 二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例:
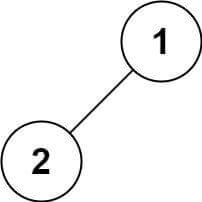
- 输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
- 输出:[1,3,2]
- 输入:root = []
- 输出:[]
- 输入:root = [1]
- 输出:[1]
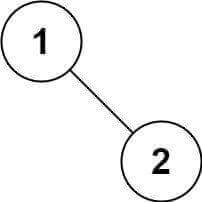
- 输入:root = [1,2]
- 输出:[2,1]
- 输入:root = [1,null,2]
- 输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围 [0, 100] 内
- -100 <= Node.val <= 100
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
// 递归版
const res = [];
const rec = (node)=>{
if(!node){
return;
}
// 中序遍历 左根右
rec(node.left); // 左子树
res.push(node.val); // 根节点
rec(node.right); // 右子树
}
rec(root);
return res;
};优化方案:
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
*/
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
// 迭代版
const res = [];
const stack = []; // 模拟递归堆栈
let point = root; // 指针
while(stack.length || point){ // 整体大循环
while(point){ // 把所有的左节点推入栈中
stack.push(point)
point= point.left;
}
const node = stack.pop(); // 访问节点,即出栈
res.push(node.val);
point = node.right; // 指针指向右节点
}
return res;
};LeetCode #112 路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例:
给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
解题思路:
- 在深度优先遍历的过程中,记录当前路径的节点值的和
- 在叶子节点处,判断当前路径的节点值的和是否等于目标值
解题步骤:
- 深度优先遍历二叉树,在叶子节点处,判断当前路径的节点值的和是否等于目标值,是九返回true
- 遍历结束,如果没有匹配到,就返回false
复杂度:
- 时间复杂度 O(n)
- 空间复杂度 O(n)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {number} sum
* @return {boolean}
*/
var hasPathSum = function(root, sum) {
if(!root){
return false;
}
let res = false;
const dfs = (node,sumAcc) => {
// console.log(node.val, sumAcc)
if(!node.left && !node.right && sumAcc === sum){
res = true;
}
if(node.left){
dfs(node.left, sumAcc + node.left.val)
}
if(node.right){
dfs(node.right, sumAcc + node.right.val)
}
}
dfs(root, root.val);
return res;
};前端与树:遍历JSON的所有节点值
用途:清洗JSON
const json = {
a: { b: { c: 1 } },
d: [1, 2]
}
const dfs = (node, path) => {
console.log(node, path); // 访问当前节点
Object.keys(node).forEach(k=>{ // 获取所有key,即所有孩子节点
dfs(node[k], path.concat(k));
})
}
dfs(json, []);前端与树:渲染Antd的树组件
// CodePen 模拟树组件
const { Tree } = antd;
const { TreeNode } = Tree;
const json = [
{
title: "一",
key: "1",
children: [{title:"三",key:"3",children:[
{title:"五",key:"5",children:[]}
]}]
},
{
title: "二",
key: "2",
children: [{title:"四",key:"4",children:[]}]
},
]
class Demo extends React.Component {
dfs = (node)=>{
return (
<TreeNode title={node.title} key={node.key}>
{node.children.map(this.dfs)}
</TreeNode>
)
}
render() {
const tProps = {
treeDefaultExpandAll: true,
style: {
width: '100%',
},
};
return (
<Tree {...tProps}>
{json.map(this.dfs)}
</Tree>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Demo />, mountNode);树-总结
- 树是一种分层数据的抽象模型,在前端广泛应用
- 树的常用操作:深度、广度优先遍历,先中后序遍历...

Comments | NOTHING