什么是树的深度/广度优先遍历?
- 深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索树的分支
- 广度优先遍历:先访问离根节点最近的节点
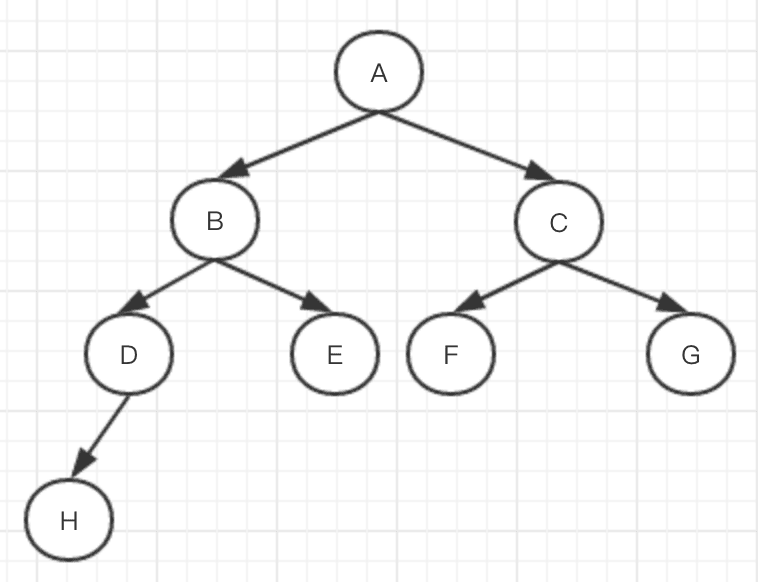
- 深度优先遍历,如上图所示,会先访问根节点A,然后沿着左树一直向下深层访问遍历,即A-B-D-H-E-C-F-G
- 广度优先遍历,如上图所示,会先访问根节点A,然后向下一层,并将该层访问遍历完毕,再继续向下一层遍历。即A-B-C-D-E-F-G-H
深度优先遍历算法
- 访问根节点
- 对根节点的children挨个进行深度优先遍历
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: []
},
{
val: 'e',
children: []
}
]
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: []
},
{
val: 'g',
children: []
}
]
}
]
}
const dfs = (root) => {
console.log(root.val);
// root.children.forEach((child)=>{
// dfs(child)
// })
// 优化写法
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
dfs(tree)
// a b d e c f g
广度优先遍历算法
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队
- 把对头出队并访问
- 把对头的children挨个入队
- 重复第二三步,知道队列为空
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: []
},
{
val: 'e',
children: []
}
]
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: []
},
{
val: 'g',
children: []
}
]
}
]
}
const bfs = (root)=>{
const queue = [root];
while(queue.length>0){
const n = queue.shift();
console.log(n.val)
n.children.forEach(child=>{
queue.push(child);
})
}
}
bfs(tree)
// a b c d e f g


Comments | NOTHING